Description And Characteristics Of Pityriasis Versicolor
The skin is the first line of defense against pathogenic microorganisms. Therefore, fungal infections such as pityriasis versicolor are one of the most common reasons for requesting dermatological consultations. In this article, we will discuss the characteristics of pityriasis versicolor.
First of all, keep in mind that a large number of microorganisms populate the surface of the skin and are part of the normal microbiota. They are harmless under normal conditions, but can cause infections in certain circumstances.
What is pityriasis versicolor?
This fungal infection of the skin, also known as Tinea versicolor, occurs due to a fungus of the genus Malassezia. According to several studies, the causative agent may vary depending on the geographical location. M. globosa is responsible for infections in temperate countries and M. furfur in tropical countries.
This disease affects people of all walks of life equally and has an almost uniform distribution worldwide. However, the infection is more common in countries with hot and humid climates. These conditions favor the multiplication of this type of fungus on the skin.
The most affected people tend to be young and there is a maximum incidence of the disease between 20 and 40 years. The causative agent colonizes the skin without causing damage; however, it can proliferate under certain conditions and lead to an infection.
Characteristics of pityriasis versicolor
As mentioned above, the infection occurs due to a fungus of the genus Malassezia, common in the skin. In fact, Malassezia furfur has been isolated in 95% of areas with numerous sebaceous glands in different individuals.
The fungus colonizes these areas because it needs fat for food. Certain factors that can change the oily composition of the skin will lead to the proliferation of the microorganism. In this way, the number of mushroom stems will increase.
The following situations may encourage the onset of pityriasis versicolor:
symptom
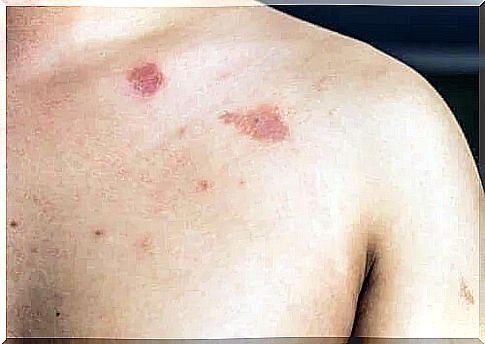
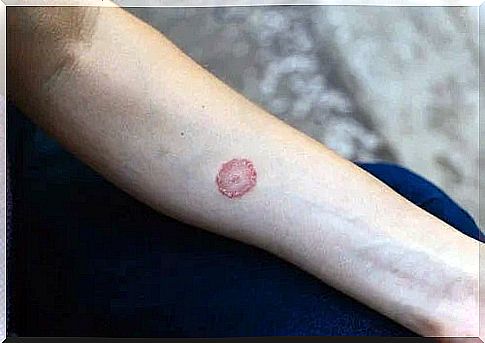
The main feature of this infection is the appearance of oval-shaped spots – scaly spots on the skin. These spots may be lighter or darker in color than the surrounding tissue and are reddish, brown or white.
Injuries can occur anywhere on the body, although they most commonly occur on the back, neck, chest and upper third of the arm. They can also appear in the folds of the skin and people can easily confuse them with psoriasis.
In addition to skin lesions, the infection is usually asymptomatic, although itching may occur in certain circumstances – sweating, for example. Remember that pityriasis versicolor is neither painful nor contagious, but it causes significant psychological discomfort.
Diagnosis of pityriasis versicolor
Now that we have established the characteristics of pityriasis versicolor, we will discuss the method of diagnosis.
Establishing the diagnosis is quite simple. Dermatologists can make an accurate diagnosis by simply looking at the skin lesions. However, this condition can be confused with other skin conditions – such as seborrheic dermatitis.
There are different tests for a differential diagnosis, although the most common is direct observation under a microscope. To do this, doctors will take a sample of the lesions, add potassium hydroxide and examine the material under a microscope.
In some cases, a culture may be needed for the sole purpose of differentiating between the types of Malassezia that could cause the infection.
Treatments for pityriasis versicolor
As mentioned above, this is a fungal infection and therefore antifungals are the right treatment. According to some medical sources, shampoos and creams are effective in most cases. Thus, physicians should reserve systemic treatment for patients experiencing relapses and failure of the usual approach.
Regarding topical treatment, the use of creams, gels or shampoos with ketoconazole or cyclopirox has been shown to be effective. In addition, the use of a 2.5% selenium sulfide shampoo is very beneficial. The lesions usually disappear within 1-2 weeks in most cases.
Systemic treatment should be used if topical treatment is not effective. In this regard, fluconazole, ketoconazole or itraconazole can be administered orally for a certain period of time.
How is pityriasis versicolor prevented?
Although it is caused by a fungus that lives on the skin, there are several measures that can be taken to prevent the appearance of this disease. Most preventative tips are aimed at maintaining proper personal hygiene and reducing the amount of sebum on the skin.
In addition, note that Tinea versicolor is recurrent. Therefore, oral intake of antifungals is recommended in the warmer months, with prior medical authorization, if you have previously been affected by these fungi.