Degenerative Joint Disease: Causes And Treatment
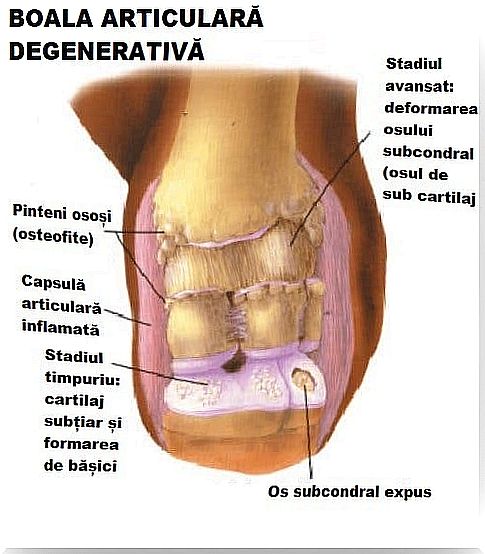
Also known as osteoarthritis, degenerative joint disease includes a number of disorders that affect the hyaline cartilage and subchondral bones. This causes pain, inflammation and prevents the execution of normal movements. Cartilage is the tissue that covers the ends of the bones, being essential for the proper functioning of the joints.
The main consequence of degenerative joint disease is damage to the articular cartilage. The bones wear out and start to hurt. As the cartilage disappears, the bones react and bone tissue forms around their ends, causing the joints to deform.
Causes of degenerative joint disease
Due to increasing life expectancy and an aging population, degenerative joint disease is expected to become the fourth leading cause of disability in 2020. No one knows the exact cause of this health problem, but certain risk factors have been identified. associated with its development:
- Age: The risk of osteoarthritis increases exponentially from the age of 50.
- Gender: Most patients are women between the ages of 50 and 55.
- Genetic inheritance: The risk of osteoarthritis can be up to 65% in people whose parents have suffered from this problem.
- Workplace activity: Repetitive tasks overload long-term joints.
- Extreme physical activity: Athletes have an increased risk of osteoarthritis.
- Menopause: Decreased estrogen levels specific to menopause are a major factor in the development of degenerative joint disease.
- Obesity: This does not appear to be a major factor in the development of osteoarthritis. But extra pounds can worsen the condition of certain joints, especially the knees.
- Fractures and injuries: May trigger degenerative joint disease.
Symptoms of degenerative joint disease
Degenerative joint disease has a gradual evolution. Initially, it affects one or more joints, evolving into a feeling of stiffness that appears in the morning. In general, this stiffness is short-lived and can be improved by movement.
As the disorder progresses, the mobility of the affected joint decreases. Contractions occur with flexion, pressure sensitivity and a “crack” sensation. Sometimes mechanical blockages also occur due to the presence of free bodies inside the damaged joint.
The symptoms of osteoarthritis are varied and develop progressively. The most common are joint pain, limited movement, friction and, in some cases, hydrarthrosis (spilled joint). Joint pain and inflammation can occur even after long periods of inactivity. Excessive growth of tissue at the ends of the bones causes deformities.
Pain is the most worrying symptom of osteoarthritis. But she tends to disappear after rest. However, as the disorder progresses, the patient may feel pain both when moving and when resting.
How to treat degenerative joint disease

The first step to treating osteoarthritis is to avoid all the factors that contribute to joint degradation. At the same time, each patient will need an exercise regimen adapted to his needs.
In the acute stages of the disease, the pain experienced worsens due to inflammation of the affected area. The patient will need anti-inflammatory and / or analgesic drugs to reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
Your doctor may prescribe other types of medications.
Chondroprotective drugs
Pharmaceuticals in this category are specially designed to treat degenerative joint disease. They act directly on the affected joints.
In addition to relieving pain and improving mobility, chondroprotective drugs can cure osteoarthritis. They contain substances such as chondroitin sulphate, glucosamine sulphate and hyaluronic acid.